Genomic Analysis¶
The Genomic Analysis module provides a user-friendly interface to analyse genomic experiments. The image below displays the Genomics module dashboard, highlighting its key functionalities.

1 - Fixed sidebar across the Genomic module, providing quick access to various functionalities.
2 - Toolbar for accessing other GPAP modules, including: Data Submission and Management (Experiment & Files, and Phenotypic Data) and Data Analysis (Genomic Analysis and Cohort Creation).
3 - Menu for selecting your desired action.
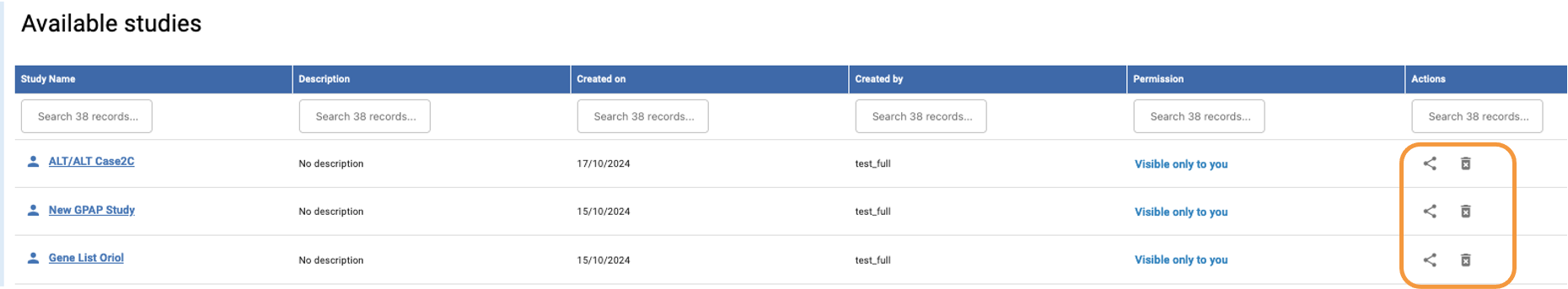
4 - Summary of your accessible saved studies
Study setup¶
The GPAP provides several types of analysis based on your specific needs:
Case Analysis: For analysing a single case or family.
Cohort Analysis: For analysing cohorts created in the CohortApp (refer to the Cohort Application section in this guidelines)
Search Across All Experiments: For searching across all accessible experiments within the GPAP.
To set up a study for your chosen type of analysis, please follow the guidelines in the corresponding section below.
Case Analysis¶
Click on the Case Analysis button in the Genomic Analysis dashboard to analyse a single case or family.
The system will guide you though the required steps for the study creation. In the following sections we describe those steps in further detail.

1. Select experiments¶
Here, you can search for an experiment, participant or family using up to five ID options. Correlations among the different IDs can be found in the Data Management module (see Experiment Data section):
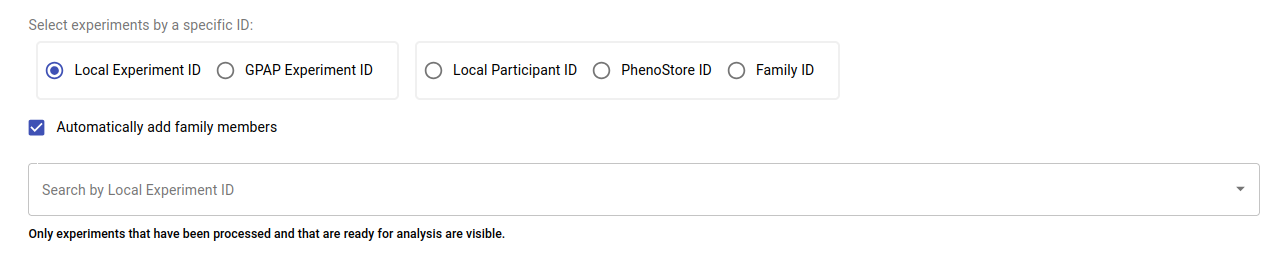
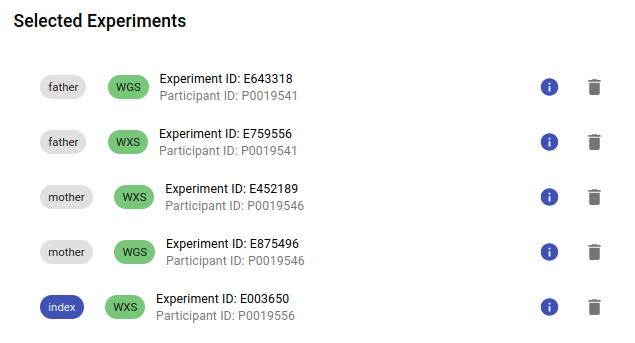
By default, the family members of any selected participant will be included in the analysis. You can disable this option by unchecking the Automatically add family members checkbox. Additionally, you can remove individual experiments from the analysis by clicking the bin icon next to each experiment, as shown in the image below.
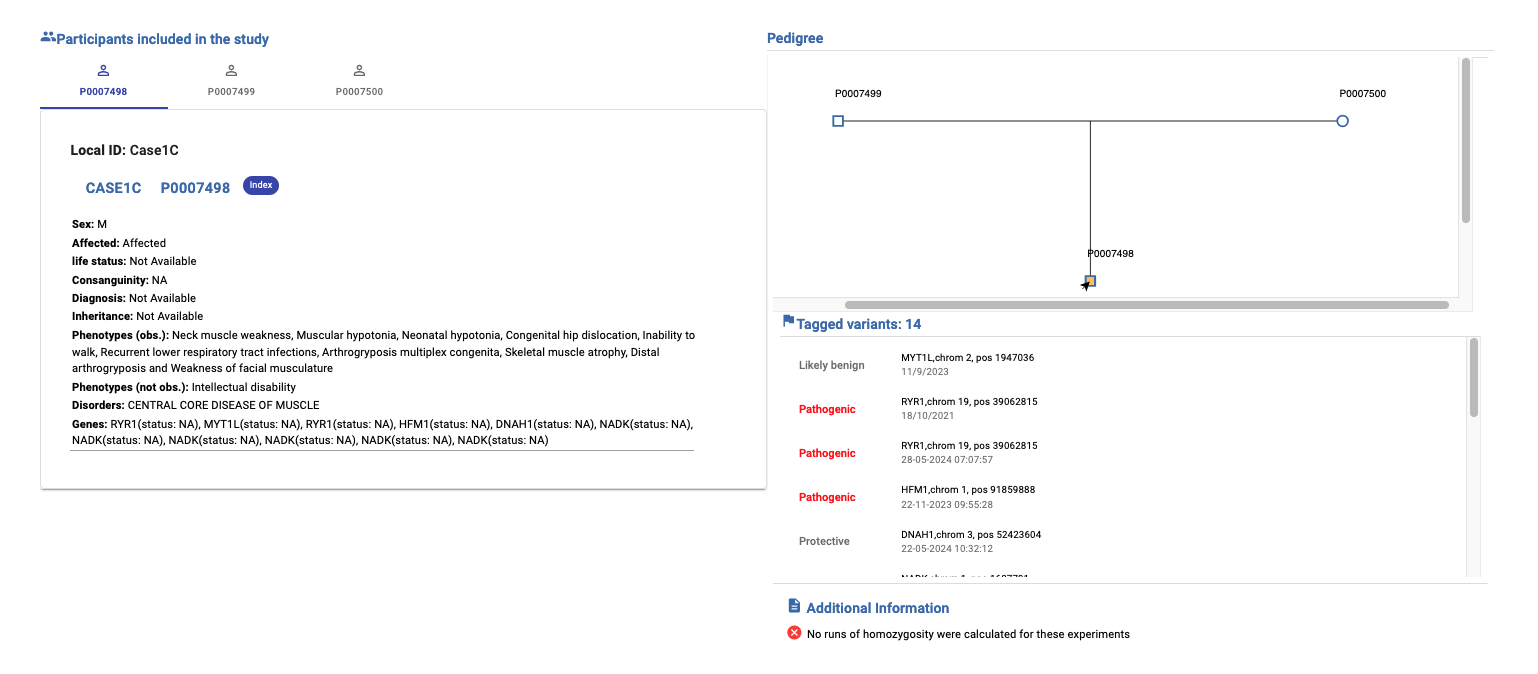
2. Review case information¶
This section provides an overview of the available information about the participants included in the study. You can review the data and access PhenoStore if you need to check or update any additional details.
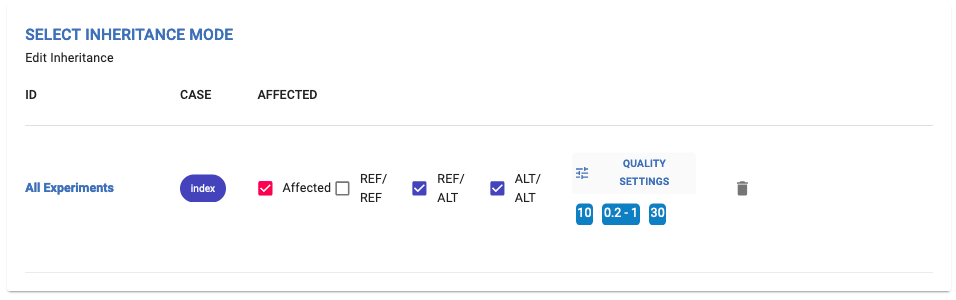
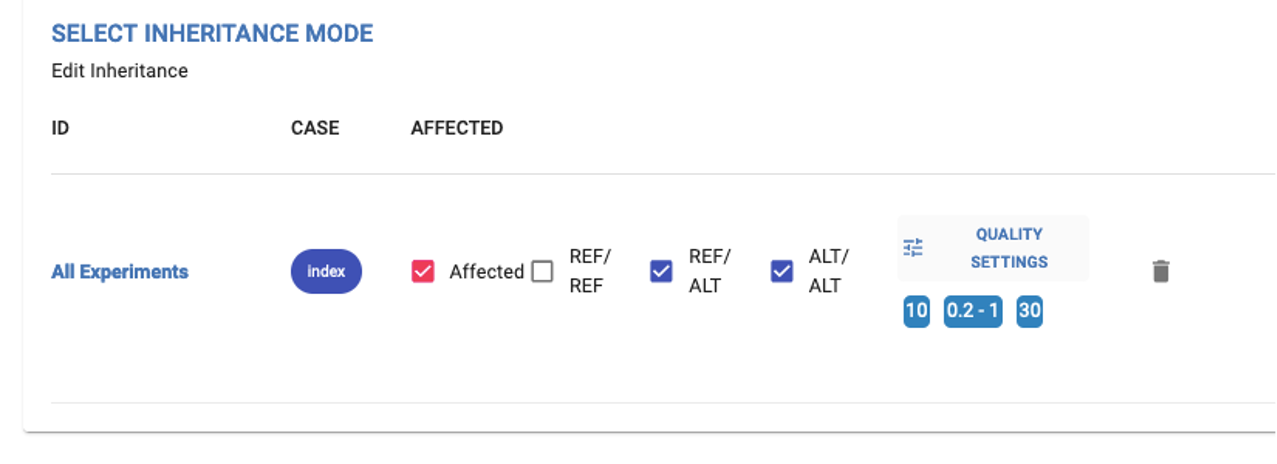
3. Select inheritance mode¶
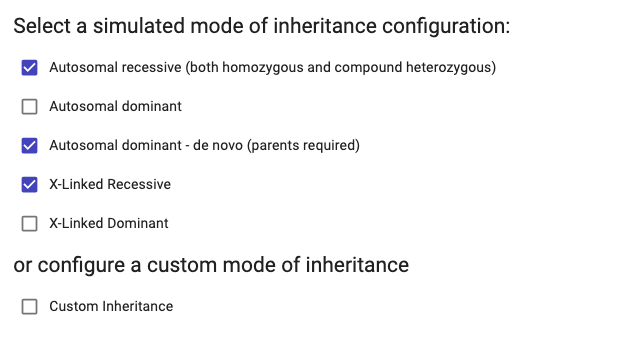
- Here, you can select here the inheritance mode(s) that you would like to assess. We offer two options:
Simulated Mode of Inheritance: Provides automatic configuration based on the recorded affected status of individuals in PhenoStore. Multiple simulated modes of inheritance can be selected.
Custom Mode of Inheritance: Allows users to select the genotype(s) to be included in the analysis. This option can be selected alongside the simulated mode.
· The compound heterozygous simulated inheritance assumes the unaffected individuals are the progenitors. The system does not currently allow testing for unaffected siblings. · The mode of inheritance is not considered for the CNV analysis.
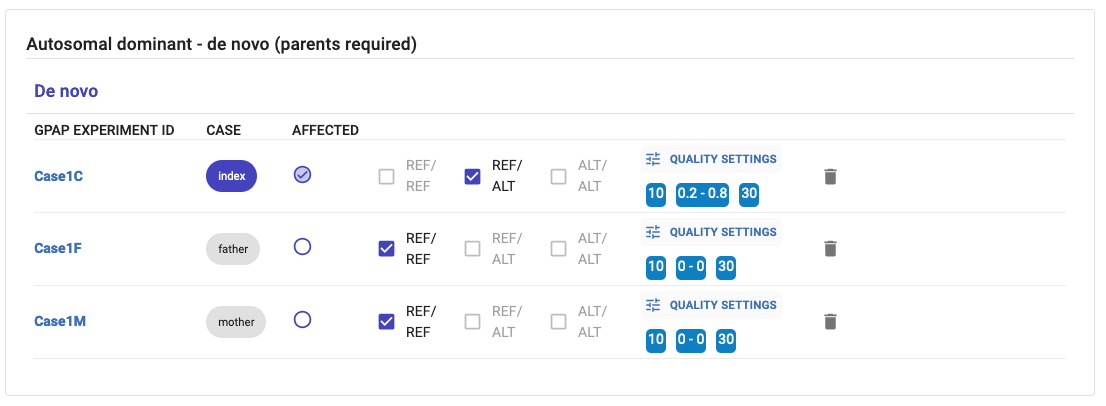
Example of simulated inheritance - Autosomal Dominant. You can only modify the quality settings. The affected statuses and the genotypes, are fixed:
Example of Custom Inheritance. The user can change the affected status of the individuals, the genotypes and the quality settings:
Quality Settings¶
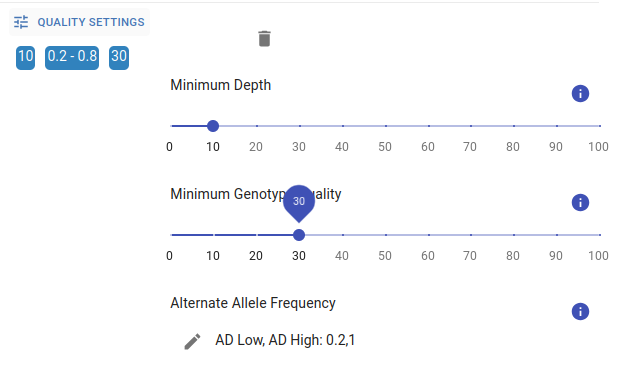
All variants with a minimum depth of coverage of 8 reads and a genotype quality (Phred-scaled) of 20 are uploaded to GPAP. A minimum depth of coverage of 10 and genotype quality of 30 for a variant position are considered by default. Alternate Allele Frequency for each inheritance mode is also shown and can be also changed by clicking on the pencil icon. All these parameters can be adjusted by using the sliders displayed in the image below.
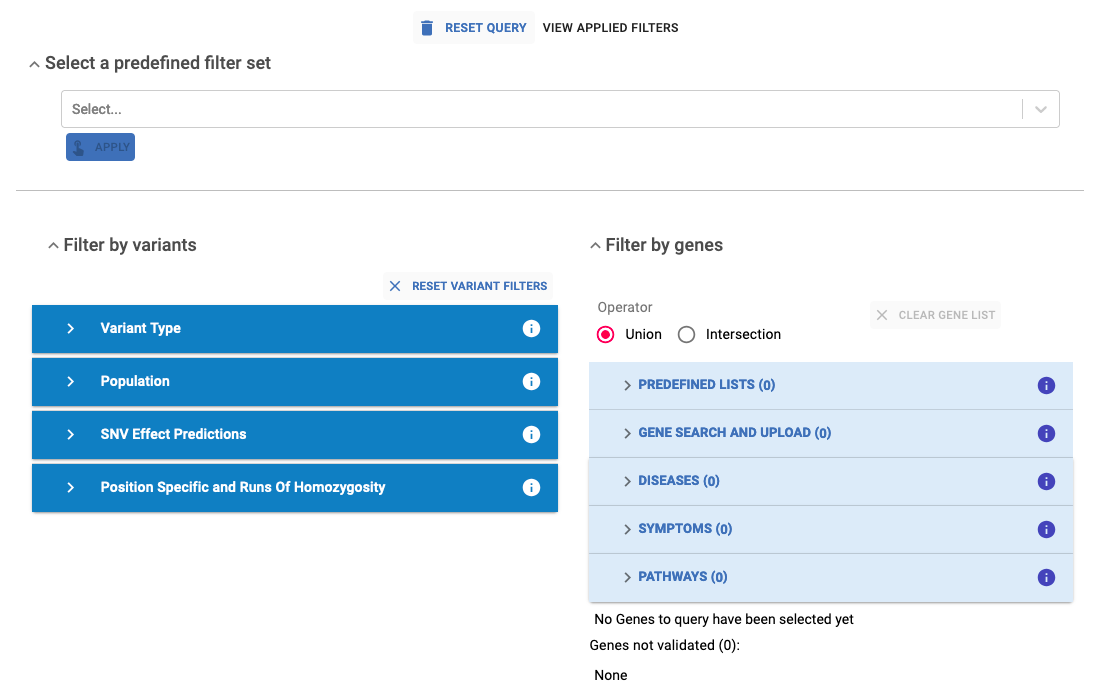
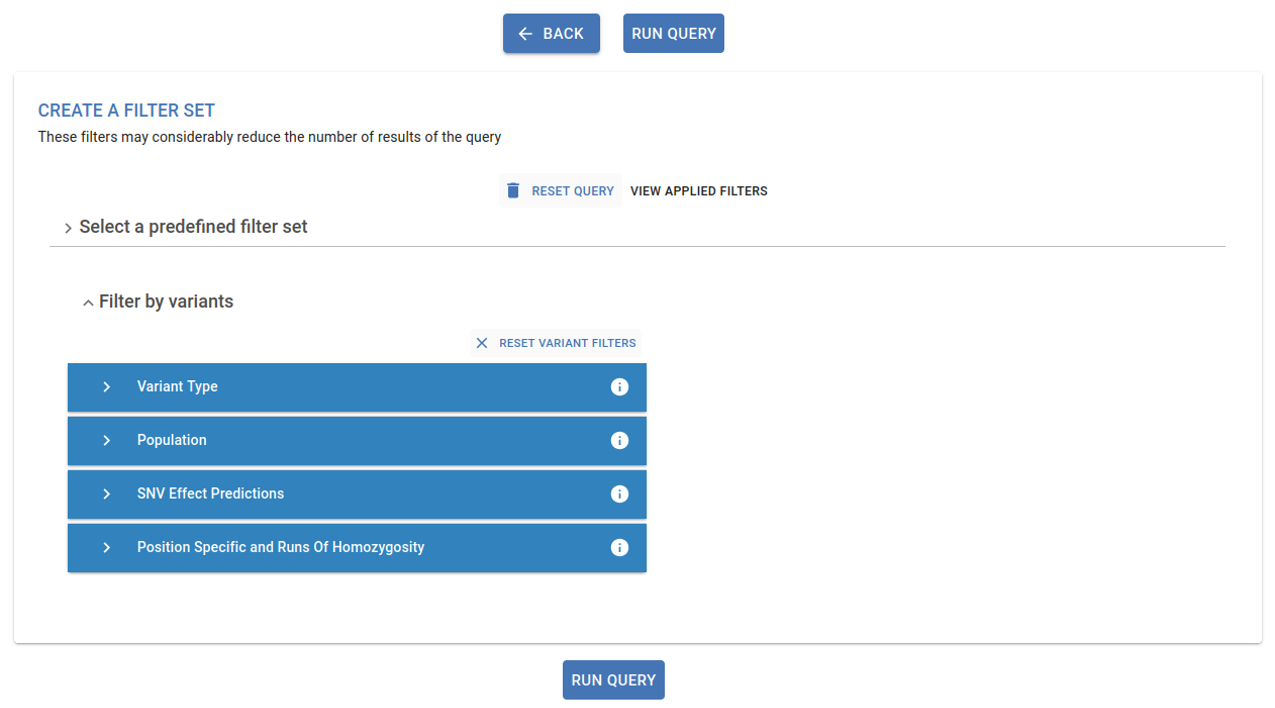
4. Apply filters¶
In this final step, you can apply various filters to narrow down the number of obtained variants. These filters are grouped into the following sections: Predefined Filter Set, Filter by Variants and Filter by Genes. Refer to the Filtering section in this guidelines for more details.
Now click on Run Query to obtain the results. Navigate to the Variant Dashboard section in this guidelines for comprehensive guidance on analysing the results.
Cohort Analysis¶
Click on the Cohort Analysis button in the Genomic Analysis dashboard to analyse cohorts previously created created in the CohortApp. Refer to the Cohort Application section in this guidelines for further details. By going through the steps described below, a study will be created.
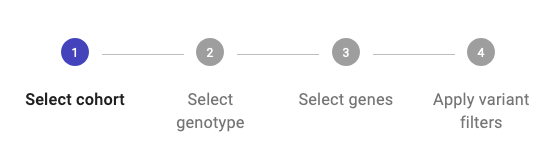
1. Select a Cohort¶
Your cohorts will be displayed in the Cohorts Ready for Analysis dropdown list. To create a new cohort, click the Go to CohortApp button and follow the instructions in the Cohort Application section of this guidelines. The new cohort will then appear in the Cohorts Ready for Analysis dropdown list. Select the desired cohort and click the Create Cohort Study button to initiate your study.
2. Select genotype:¶
Select the genotype(s) and quality settings you want to consider for your analysis (same as the Custom Mode of Inheritance configuration in the Case Analysis use case).
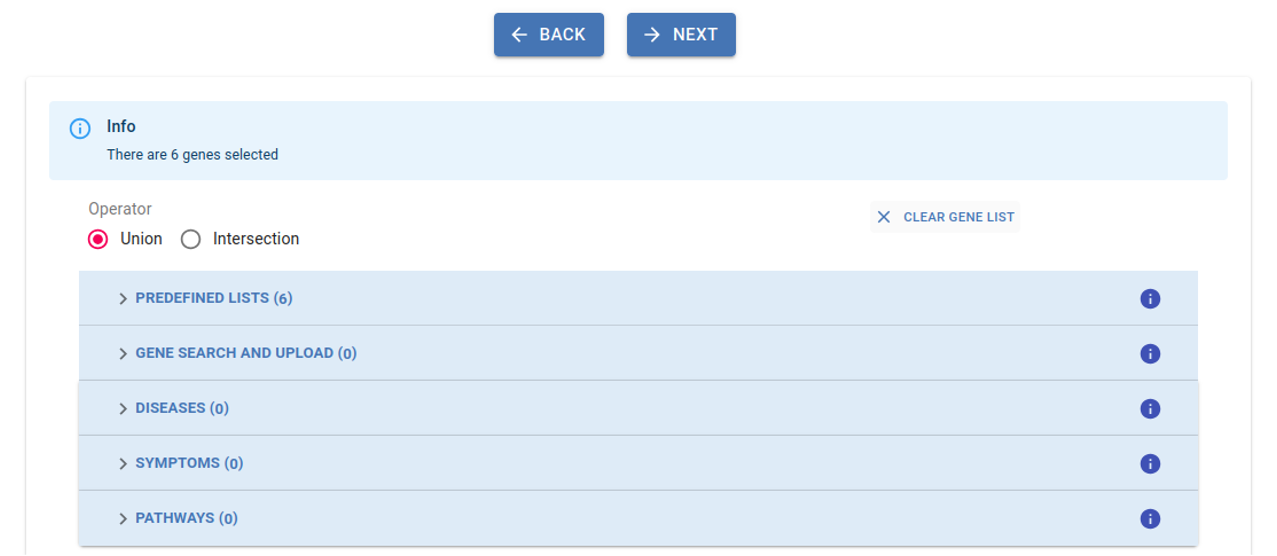
3. Select Genes:¶
Select gene(s) or gene list(s) from the different sections to narrow down the number of obtained variants, with the inclusion of at least one gene being mandatory for the analysis. By default, the union of selected genes is considered, but you also have the option to apply the intersection among gene lists from different sections. Refer to the Filtering section in this guidelines for more details.
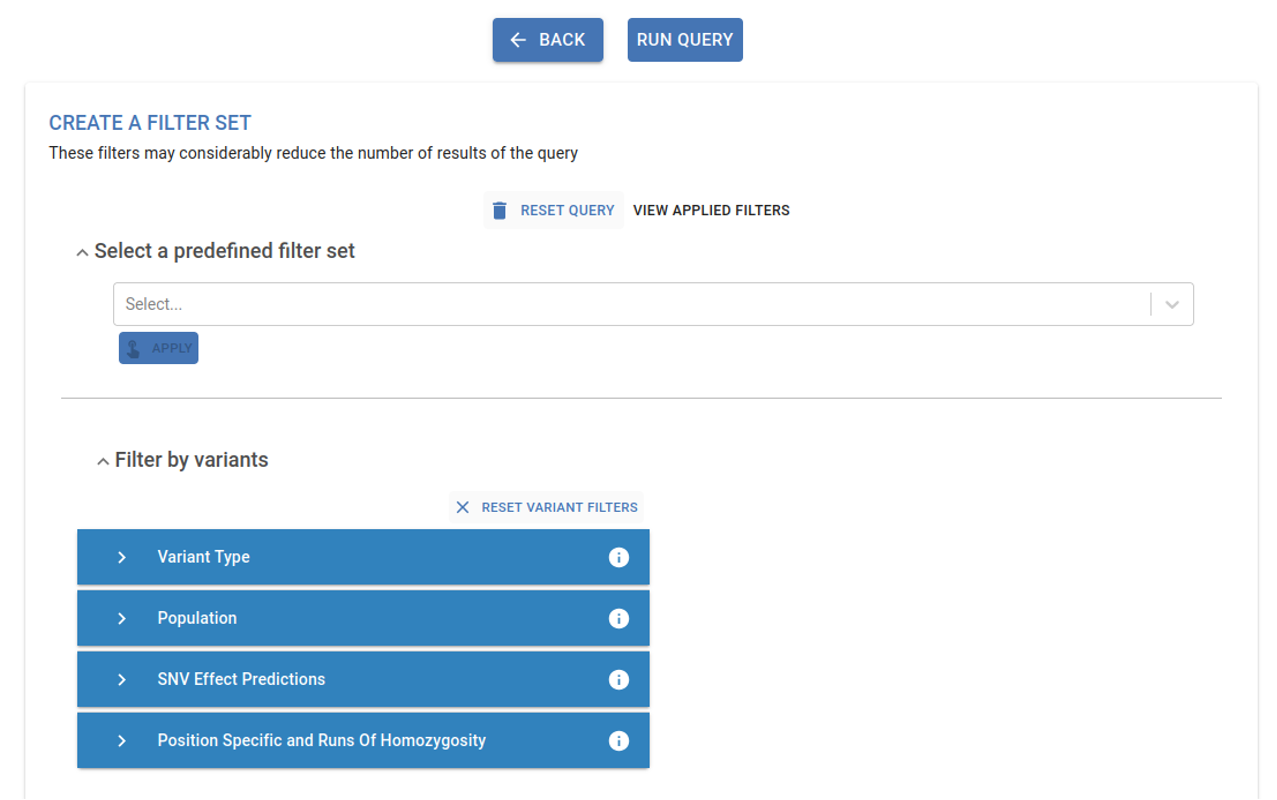
4. Apply variant filters:¶
You can now apply variant filters, which we strongly recommend to narrow down the obtained results and minimize computational effort. Please refer to the Filtering section in this guidelines for further details.
Now click on Run Query to obtain the results. Navigate to the Variant Dashboard section in this guidelines for comprehensive guidance on analysing the results.
Search Across All¶
Click on the Search Across All Experiments button in the Genomic Analysis dashboard to create a new study that allows you to search across all your accessible experiments.
Warning
This use case may lead to system performance issues when millions of variants are returned
To run a search across all your experiments, you have to go through the following three steps:

1. Select genotype¶
Select the genotype(s) and quality settings you want to consider for your analysis (same as the Custom Mode of Inheritance configuration in the Case Analysis use case).
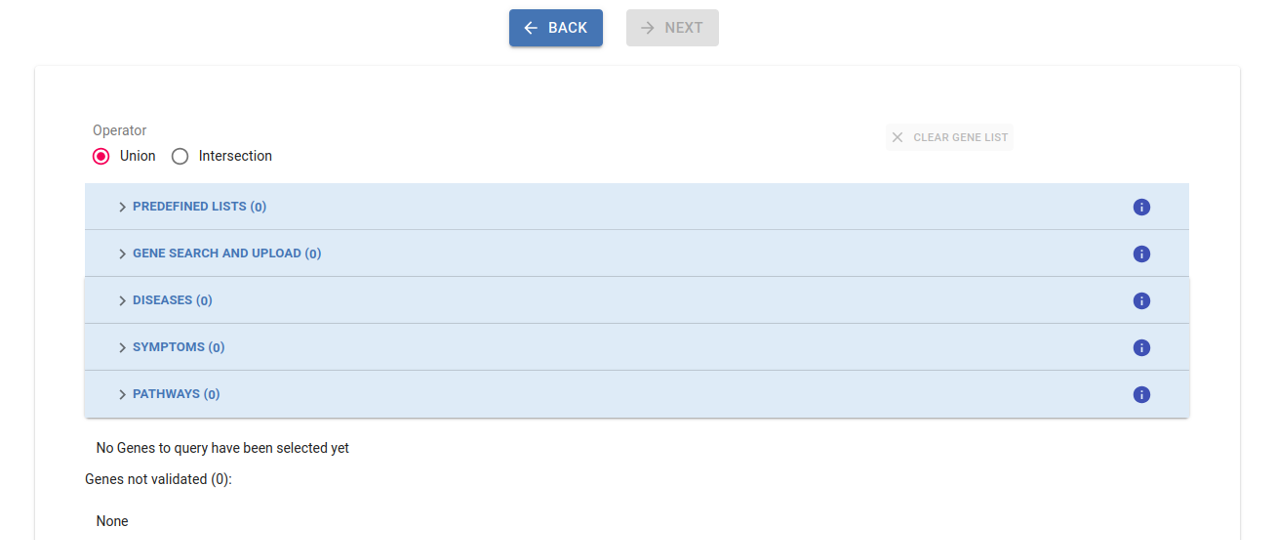
2. Select genes¶
Select gene(s) or gene list(s) from the different sections to narrow down the number of obtained variants, with the inclusion of at least one gene being mandatory for the analysis. By default, the union of selected genes is considered, but you also have the option to apply the intersection among gene lists from different sections. Refer to the Filtering section in this guidelines for more details.
3. Apply variant filters¶
You can now apply variant filters, which we strongly recommend to narrow down the obtained results and minimize computational effort. Please refer to the Filtering section in this guidelines for further details.
Now click on Run Query to obtain the results. Navigate to the Variant Dashboard section in this guidelines for comprehensive guidance on analysing the results.
Filtering¶
The genomics analysis provides different filters that can be used to narrow down results and candidate pathogenic variants. Those filters are grouped in the following sections: Predefined filter set, Filter by variants and Filter by genes
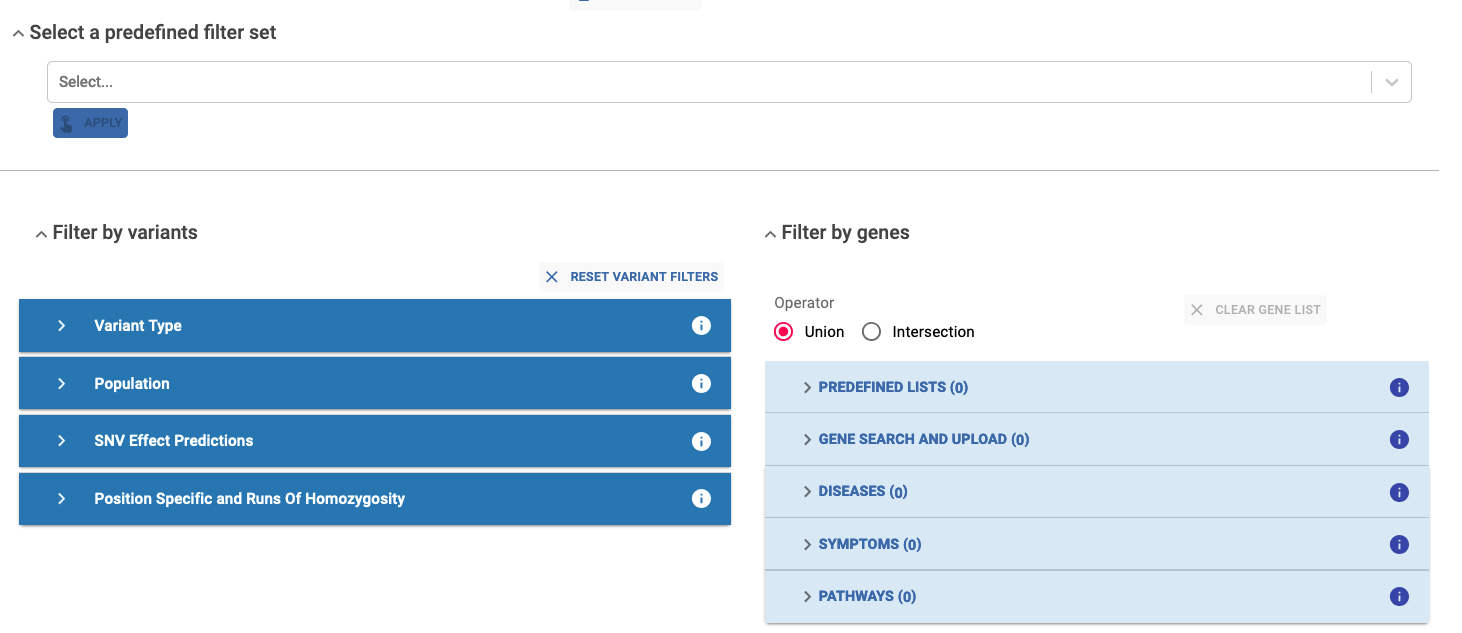
Predefined filter set¶
Specific set of predefined filters for a high, medium, or low stringency analysis. Applying one of these options automatically sets up filters in the Filter by variant section.
Variant Filters¶
Variant Type:¶
Protein Impact, as defined by Variant Effect Predictor (VEP)
Variant Consequence, as defined by Variant Effect Predictor (VEP)
ClinVar Classification: ClinVar aggregates information about genomic variation and its relationship to human health
Variant Type (SNV or Indel)
Tagged Variants (filter by tagged variants from all Experiments or only selected)
Transcript Biotype (Coding, RNA, Other)
MANE (Mane Select)
Population:¶
GnomAD AF
Internal Frequency
SNV Effect Predictions:¶
Mutation Taster
SIFT
Polyphen2 hvar
InterVAR
CADD Prediction
Revel Prediction
SpliceAI Prediction
Position Specific and Run of Homozygosity:¶
Chromosome, Start Position and End Position
Upload Bed File
Upload Coordinate file
Minimum run of homozygosity length
Gene Filters¶
Genes can be found using several search criteria:
Predefined Gene Lists
Gene Search and Upload(HGNC Database, https://www.genenames.org/)
- Disease Related Genes:
OMIM : https://omim.org/
Genomics England PanelApp : https://panelapp.genomicsengland.co.uk/
- Symptoms - HPO: https://hpo.jax.org/
Extract HPO from analysed participants. The HPOs entered in PhenoStore are automatically displayed and can be removed
Search for HPOs
After selecting the HPOs, the associated genes can be collected with the HPO database or the DisGenet database. You can then apply an internal intersection inside this section.
Pathways - from Reactome: https://reactome.org/
By default, the union of selected genes is considered, but you also have the option to apply the intersection among gene lists from different sections. During the filter creation process you can clear the gene list at any time and start over again by clicking the Clear Gene List button.
Variant Dashboard¶
The Variant Dashboard is a comprehensive interface designed to streamline the analysis of genetic variants, providing tools to efficiently explore and interpret the results.
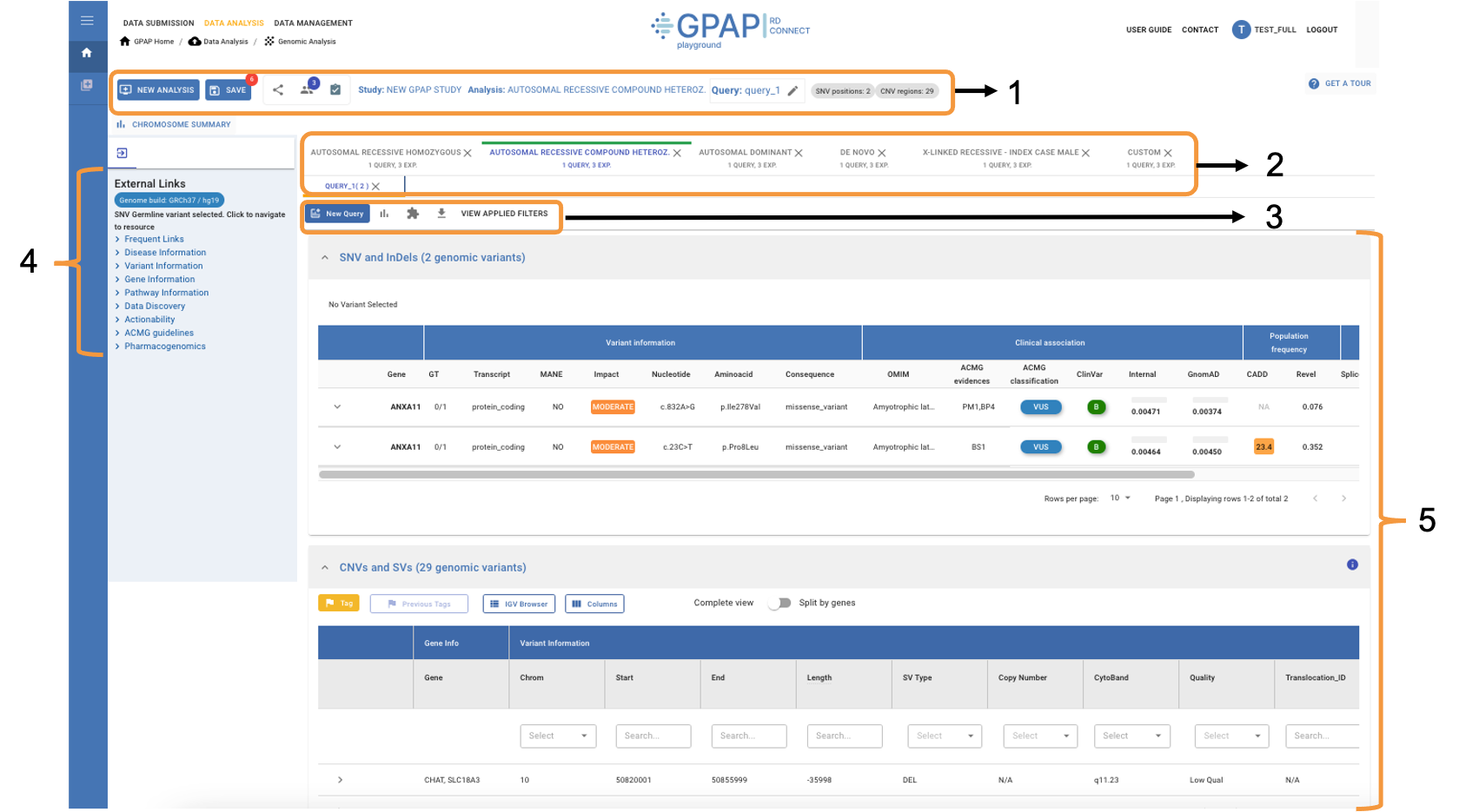
1 - Study Toolbar 2 - Analysis and Query Tabs 3 - Variant Table Toolbar 4 - External Links and Databases 5 - Results Table
Study Toolbar¶
In this study header you can find the main information about your study and perform the following actions:
New Analysis: to create a new analysis which implies edit the experiments’ genotypes and creating new queries.
Save (Study): In case you have created new queries and they’re not saved, a number will be displayed on the upper-right corner of the Save button as you can see in the image below. Please, refer to the specific section in this guidelines for further details.
Share Study: For sharing your work with other users via a url. You need to save the study prior to be able to share it.
View Participants/Experiment Information: Reviewing the main information of the analysed participants.
Analysis Status: to keep track of the status of experiments, you can change it to Analysed or Solved for a specific experiment (this feature is only available for Case Analysis use case).
Edit Query Name: Changing the name of the current query can be done at any time.
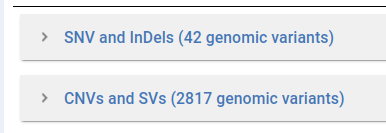
Number of variants in current query: Displayed by the query name. The SNV-InDel number corresponds to the number of genomic positions and the CNV region number corresponds to the sum of CNVs in both complete and split by genes views.
Analysis and Query Tabs¶
A separate tab is displayed for each tested inheritance mode (Analysis tabs), with nested tabs for each filtering set applied to that inheritance mode (Query tabs). Each query tab shows the number of SNVs and Indels identified.
Click New Analysis in the Study Toolbar to add an inheritance mode to the current study, and New Query in the Variant Table toolbar to add another query to the current inheritance mode. You can switch between the tabs to revisit the results and also discard queries or analyses by clicking the X button on the tabs. Click View Applied Filters, to see which filters were used in each query.
Variant Table Toolbar¶
The variant table has its own buttons set so you can do the following actions:
New Query: You can create new queries at any time by applying variant filters and using gene lists.
Summary of results: Shows a visual summary of relevant information for the collected variants.
Plugins: A list of integrated plugins that can be used by taking the variants as input such as Varsomeapi (personal VarSome API token required) and Exomiser & Genomiser
Export: Allows you exporting a maximum of 1000 variants. It will download a .csv file to your local downloads folder.
View Applied Filters: You can check on the applied filters for the current query.
External Links and Databases¶
The following links provide additional resources and tools to enhance your analysis and understanding of the variants. Select a variant from the Results Table to view the available links.
- Links:
Frequent Links: dbSNP, gnomAD, ClinVar, VarSome, HGMD, USCS, OMIM, Franklin
Disease Information: OMIM, ClinVar, DisGENET, Edgar
Variant Information: dbSNP, Ensembl, NCBI, DGVa, GWASCentral, ClinVar, gnomAD, gnomAD Rare, UCSC, Franklin, VarSome, SpliceAI Lookup, Trap Score, Wintervar, LOVD
Gene Information: Ensembl, PubMed, Entrez, GeneCards, COSMIC, GTEx, gnomAD, GWAS Central, ATLAS, eDGAR, ClinGen, HGMD, GeneReviews, LOVD, genomeRNAi, DisGeNet
Pathway Information: Wikipathways
Data Discovery: GA4GH beacon, PubCaseFinder
Actionability: Treatabolome DB, IEMbase, ClinGen Knowledge Repo
ACMG guidelines: Varsome, Franklin, Wintervar
Pharmacogenomics: PharmGKB, PharmVar
- External Databases:
Pathways Reactome
HPSCreg
HmtDB - Human Mitochondrial Database
Results Table¶
The Results Table displays the variants that meet the applied filtering criteria and is slightly different depending on the analysis performed.
Variants are grouped in two separate tables based on their type.
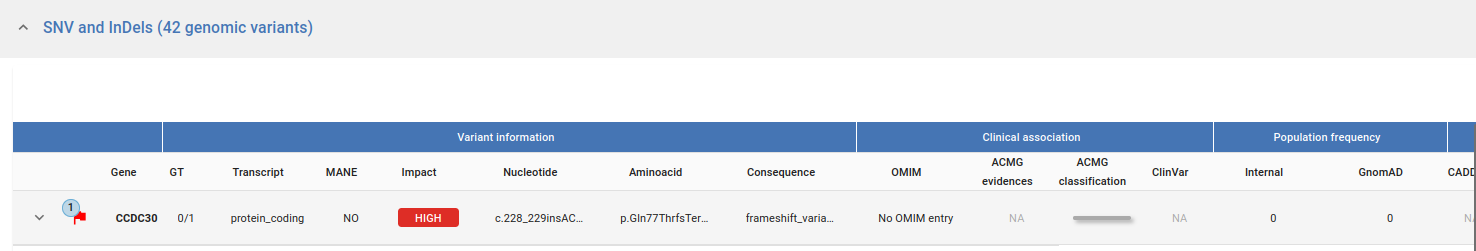
In the Variant table each row is a variant retrieved from the GPAP database. We provide information through the following fields:
Gene and Variant Info:
Gene Name
Genotype (GT)
Transcript BioType
MANE
Impact (as defined by Variant Effect Predictor (VEP))
Nucleotide Change
Aminoacid Change
Consequence (as defined by Variant Effect Predictor (VEP))
- Clinical Association:
OMIM
ACMG evidence (for SNVs only and based on InterVar)
ACMG classification (for SNVs only and based on InterVar)
ClinVar
- Population Info:
Internal Frequency
GnomAD AF
- Predictors:
CADD Predictor
Revel
SpliceAI
SIFT Pred
PolyPhen2 Hvar Predictor
Mutation Taster Predictor
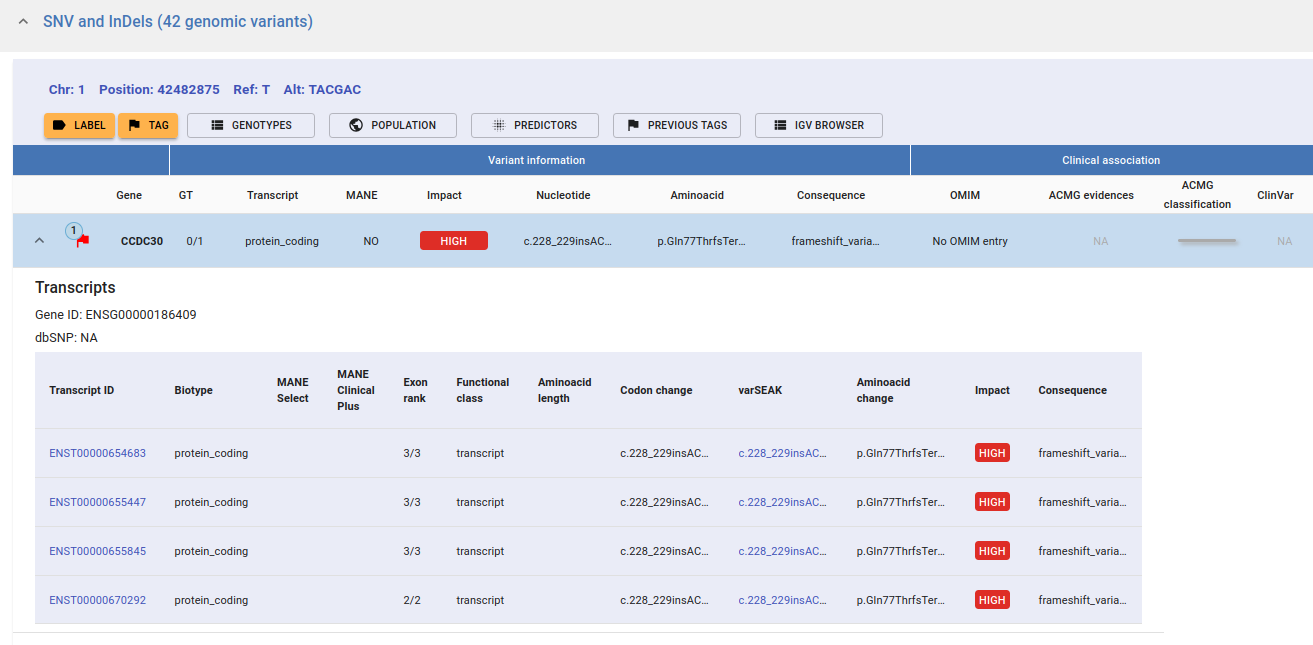
When selectiong a variant, an extra toolbar with the following options appears (see image below):
Label (refer to Label and Tag a variant section)
Tag (refer to Label and Tag a variant section)
Genotypes: genotype of the variant in all the study members
Population: allele frequencies by population
Predictors: detailed value of all pathogenicity predictors
Previous tags (refer to Label and Tag a variant section)
IGV browser: visualise the variant at IGV within a 20bp or 1kbp window.
You can get further information by selecting a variant and expanding the Variant Row. The transcripts associated with the variant will be displayed. The main information of each transcript is shown in the image below.
The CNV and SV variants are displayed in an interactive table. Every column is filterable and sortable in its header. Hovering over the column header provides additional details about the displayed information. You can swap between two existing views. The Complete View and the Split View, by using the following switch:

The Complete View shows the entire CNV or SV as detected by the caller while the Split by genes View breaks down each variant into its constituent genes displaying one gene per row.
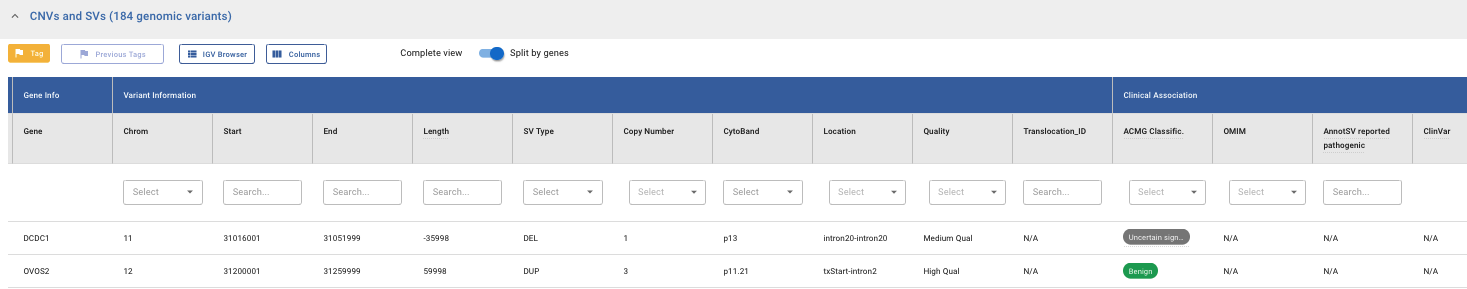
The sections and fields in the table are the following:
- Gene and Variant Info:
Gene Name
Chromosome
Start
End
Length
SV type
Copy Number
Cytoband
Location (only in split view)
Quality (see Data quality section)
Translocation_ID (groups the variants belonging to the same translocation)
Clinical Association:
ACMG Classification
OMIM (only in split view)
AnnotSV reported pathogenic
ClinVar (see ClinVar section)
Population Frequency:
AnnotSV population AFMax
Internal Frequency (see Internal Frequency section)
Internal Frequency Count: number of times a CNV / SV has been detected in our internal database (see Internal Frequency section)
Exact match
Additional Information
Tool
Experiment ID
You can get further information on a variant by clicking on the expand icon as seen in the image below.
This section is currently being developed.
Label and Tag a variant¶
When selecting a variant, two options to highlight variants are provided: Label and Tagg. Their behavior is slightly different, you can Tag a variant with a Label but you can’t label an already tagged variant.
Labeling¶
Labeling a variant is a personal annotation that will not be shared beyond the current query. By clicking on the Label button as shown in the image below, you can pick between four different labels: Important, Follow-up, Discarded and Candidate, each with its own symbol.
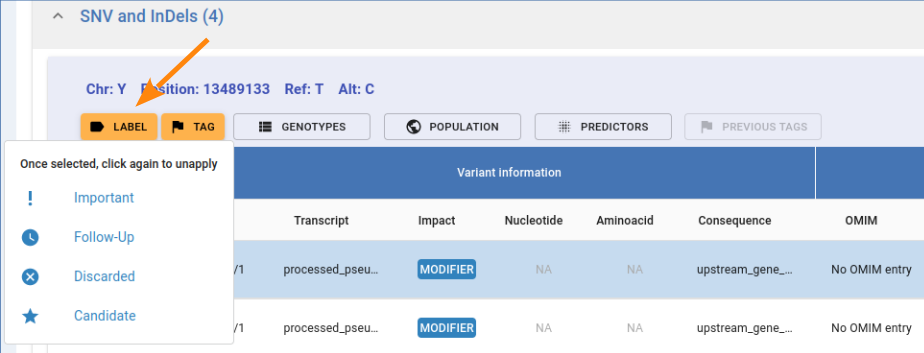
Tagging¶
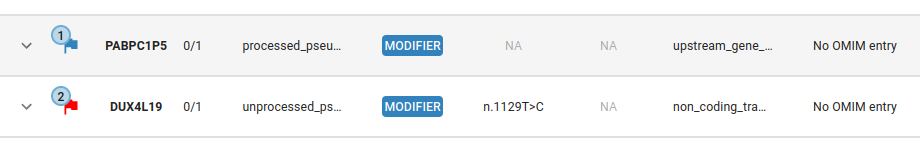
Tagging is stored within the GPAP and applies to all experiments with the tagged variant, making it visible to all GPAP users. It is indicated with a flag next to the gene name.
To tag a variant select the variant in the table and click on the tag button. The dialog in the image below will appear, fill in the different fields and indicate if this is a causative variant.

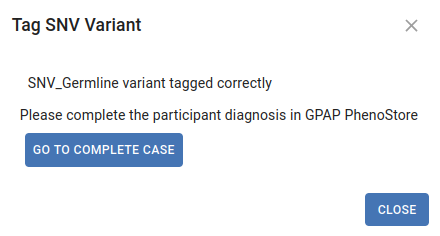
Once the tag is submitted, this dialog will be displayed:
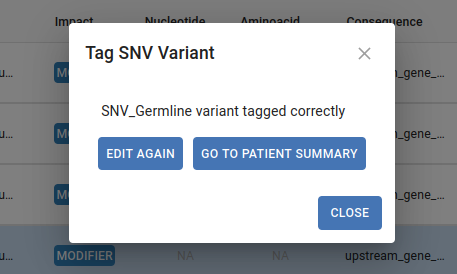
Click Go to patient summary to access PhenoStore and edit the case information. If the Causative checkbox is selected and you are the owner of the case, you will be requested to update the Participant’s Solved Status.
The number in the upper-left corner of the tag flag indicates how many times this variant has been tagged. Hovering over the flag displays a tooltip with the sample code and the clinical significance/s of each tag.
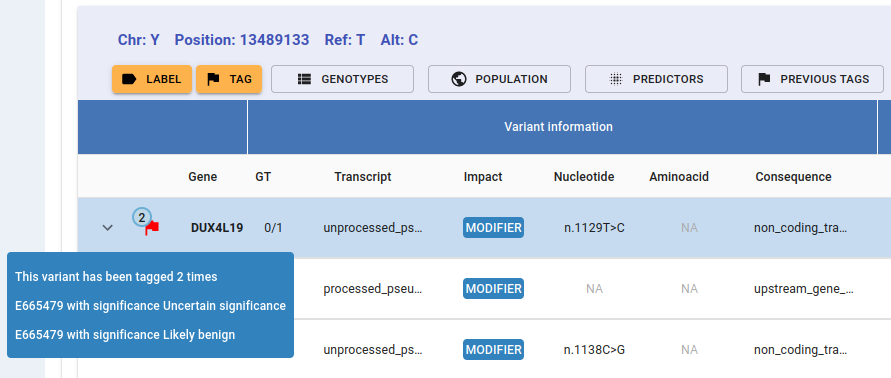
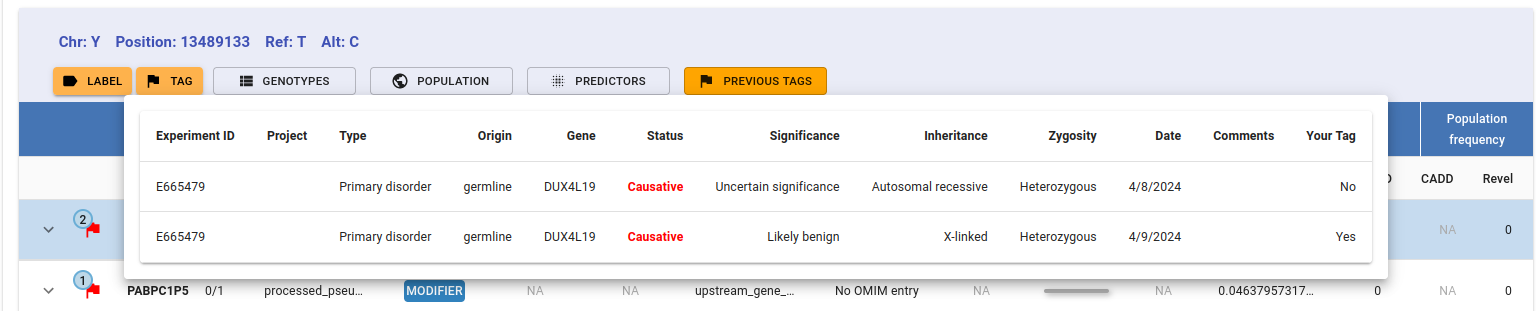
If you still need further details on the other users’ tags, click on the Previous Tags button and a detailed list will unfold:
CNV/SV analysis¶
This section provides an overview of the CNV and SV analyses conducted, highlighting the tools used, key considerations, and their implications for interpreting CNV and SV results.
Note
SVs that fail the quality check or exceed 10 Kb in lenght are not uploaded to the GPAP.
A maximum of 10,000 CNVs + SVs per individual are displayed. If more than 10,000 meet the filtering criteria, only the first 10,000, sorted by chromosomal order, will be shown.
Workflow¶
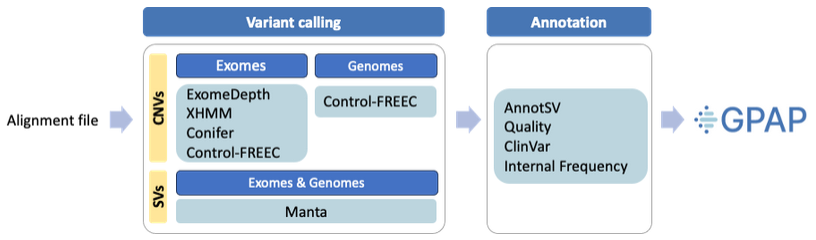
Variant calling tools¶
ExomeDepth, XHMM and Conifer: Used specifically for CNV detection in exomes. A minimum of 10 individuals sequenced with the same kit are needed for conducting the CNV analysis. To enhance performance and mitigate technical noise, all available individuals sequenced with the same kit are analyzed collectively.
Control-FREEC: For calling CNVs from both exomes and genomes. A sliding window size of 20000bp is considered by comparing each individual to a baseline generated from a minimum of 50 sex-matched individuals sequenced under the same conditions.
Manta: Used for SV calling in both exomes and genomes. Detected variant classes include deletions, insertions (fully and partially assembled), inversions, tandem duplications and interchromosomal translocations. It’s based on paired and split-read evidence, although it does not require split-reads or successful breakpoint assemblies to report a variant in cases with strong evidence.
Annotation¶
AnnotSV is used to annotate and harmonize the outputs of all the CNV/SV callers. This tool provides functional, regulatory and clinical annotations for CNV/SV interpretation. The most relevant annotations will be displayed in the GPAP main results table.
Data quality¶
The following quality parameters are considered for each CNV/SV caller:
CNV/SV caller |
Quality parameter |
|
|---|---|---|
CNVs |
ExomeDepth |
Bayes Factor |
Correlation Coefficient |
||
XHMM |
Q_SOME |
|
Q_NON_DIPLOID |
||
Conifer |
Standard deviation |
|
Control-FREEC |
Wilcoxon P-value |
|
Kolmogorov-Smirnov P-value |
||
SVs |
Manta |
Phred score (QUAL) |
Filter |
CNVs are ranked based on the parameters outlined in the Table above. In tools where multiple quality parameters are available, each one is individually ranked before being combined. Then, CNVs are categorized into quartiles as follows:
HIGH confidence: CNVs in the first quartile
MEDIUM confidence: CNVs in the second and third quartile
LOW confidence: CNVs in the fourth quartile
For SV, those SVs with the highest quality (Phred Score = 999 and Filter = PASS) are classified as HIGH confidence. The remaining SVs are ranked based on Phred score and Filter parameters and classified into quartiles following the CNVs approach. It is important to note that the employed CNV/SV callers do not propose specific thresholds to distinguish genuine CNVs/SVs from false positives. Our quartile classification approach is meant to be a guide for CNV/SV interpretation.
ClinVar¶
CNV/SV data is annotated with ClinVar considering 2 different overlaps depending on the clinical significance of the ClinVar feature (based on AnnotSV guidelines):
Features overlapping the test variant: at least 70% of the test variant overlaps with a benign or likely benign feature in ClinVar.

Features overlapped with the test variant: at least 70% of the ClinVar NOT benign and NOT likely benign feature overlaps with the test CNV.

ClinVar annotation is limited to variants with precise genomic location, mapped to the GRCh37 and/or GRCh38 genome assembly and <10Kb in length. Variants with imprecise start and stop, such as CNVs detected by microarray or translocations are not included in ClinVar’s VCF files and therefore can’t be annotated.
Internal Frequency¶
Internal frequency of each CNV/SV in our in-house database is computed considering that two events are the same if:
They are the same CNV/ SV type
They have at least 70% reciprocal overlap
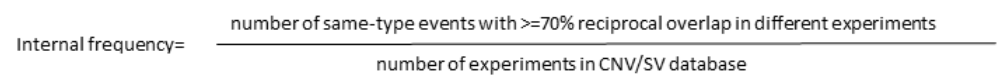
For translocations:
Patient Matchmaking¶
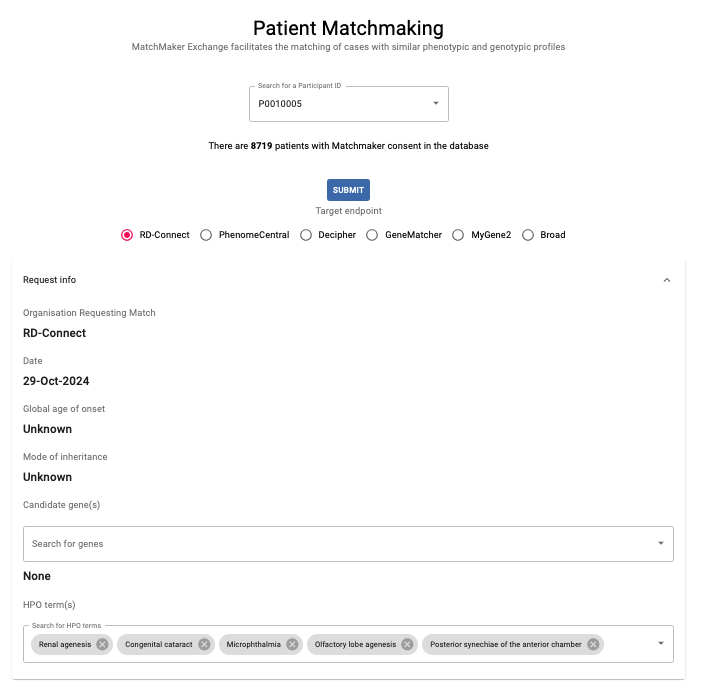
Click on the Patient Matchmaking button in the Genomic Analysis dashboard to use MatchMaker Exchange (MME) to find patients with similar phenotypic and genotypic profiles in other databases.
Search for the PhenoStore ID of your patient of interest in the dropdown list; all patients with Matchmaker consent are included. To submit the Matchmaker request, choose a database and complete the candidate gene(s) and HPOs if needed (note that the patient HPOs are imported from PhenoStore).
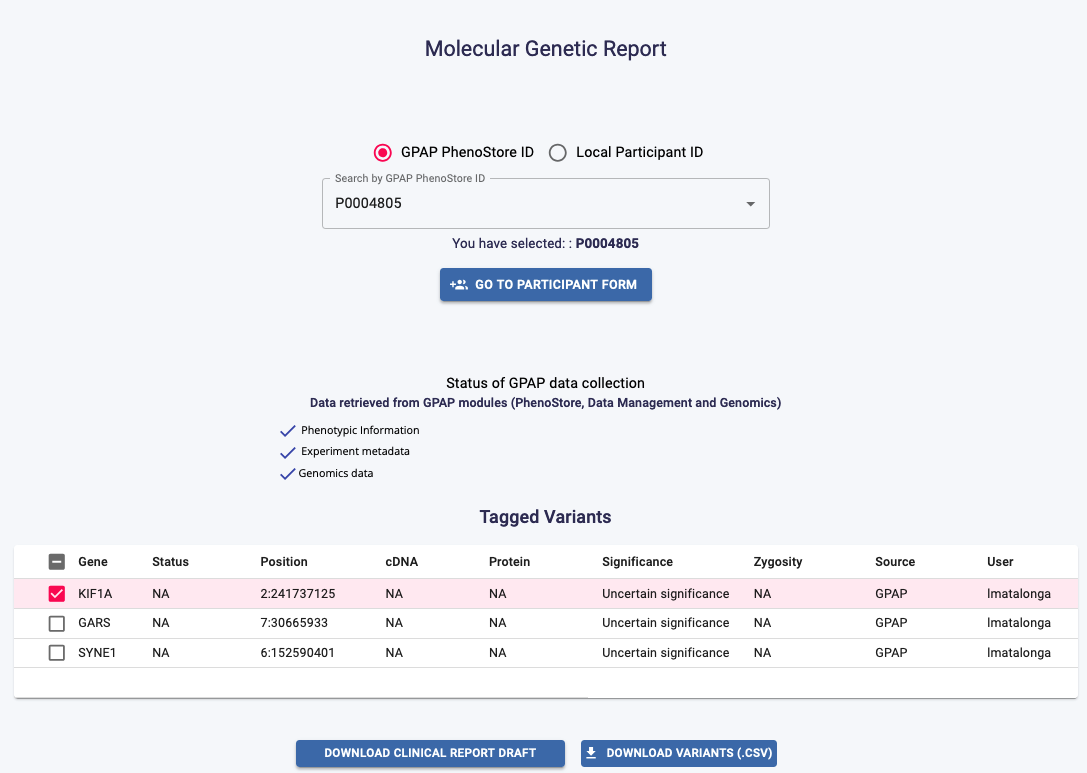
Clinical Report¶
Click on the Clinical Report button in the Genomic Analysis dashboard to create and export a draft of a clinical report.
Search for the PhenoStore ID or Local Participant ID in the dropdown list. Phenotypic information, experiment metadata and genomics data will be retrived from the corresponding GPAP modules. Select the tagged variants you want to include and choose to either Download a Clinical Report Draft or to Download Variants (.CSV).